
A recent community-driven white paper, whose writing was led in part by members of the NSD, surveys the advanced nuclear physics computing landscape, identifying opportunities for both the research community and the funding agencies to exploit such developments.

In December, NSD held the second annual offsite retreat during which the whole division came together to hear updates from the scientific programs, and discuss topics including career development, outreach and communication, and cross-divisional collaboration.
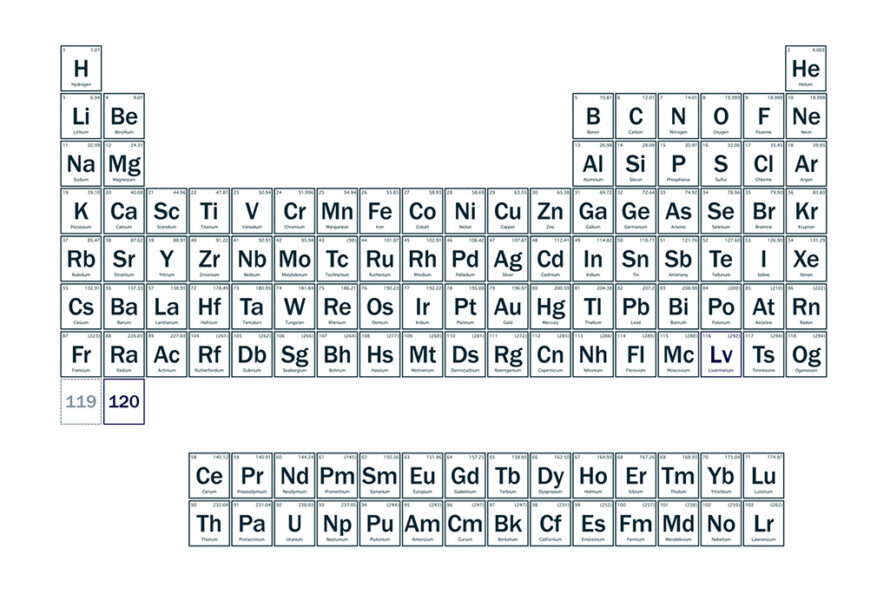
A major breakthrough in our heavy element program was achieved and published, with the first production of a superheavy element, Livermorium (Z=116), using a 50Ti beam. Find out more in this issue about how this achievement opens the door to search for Element 120.

The goats are back at the Lab, so it must be summer. It is also the time to welcome nine summer interns who are working with teams across the Division. There was much to celebrate since the last newsletter.
It was wonderful to learn that Alan Poon is among five Berkeley Lab researchers elected into the 2023 class of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Heartfelt congratulations to Alan and all 2023 AAAS fellows.
2023 has been an important year for Nuclear Science in the U.S. with the roll out of the new NSAC Long Range Plan (LRP) on Nuclear Science “A New Era of Discovery”.

Fall is kicking off with major developments. The Nuclear Science community is rolling out its new Long Range Plan for Nuclear Science with ambitious scientific and technical goals and clear priorities for the years ahead…

This issue provides insights on why coherent photonuclear interactions in ultra-peripheral collisions (UPCs) at ALICE and STAR provide physics opportunities while also presenting a puzzle for our theoretical understanding of…

In this issue of the NSD Newsletter we learn about exciting theoretical studies by the NSD theory group of Mach cones that are produced by jets in high-energy heavy-ion collisions and provide insights on the equation of state and shear viscosity…
2023 promises to be an exciting year. The U.S. nuclear science community, with strong involvement by division members, is developing its new NSAC Long Range Plan. Major projects of the division are advancing with GRETA moving into…

The 88-Inch Cyclotron facility provides high-intensity, medium-charge-state ions as well as low-intensity, high-charge-state ion beams to its users. The positively charged ion beams are used for experiments ranging from Super Heavy Element searches…
The Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) officially began operations and started its user program in May. A ribbon-cutting ceremony was held May 2, 2022 to officially mark the “start of FRIB’s scientific mission” with U. S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm and the…

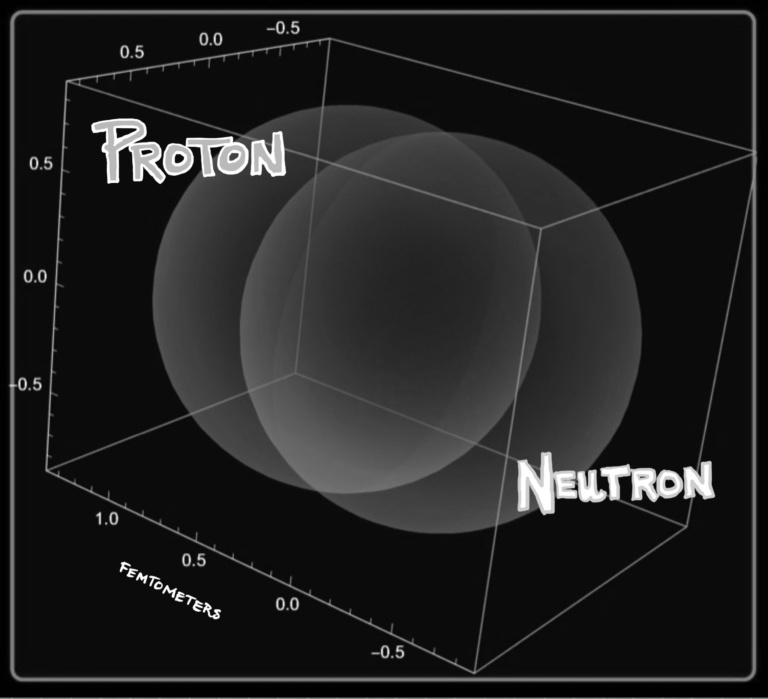
The building blocks of matter, protons, and neutrons, are made of quarks and held together by gluons. Each of these objects – quarks, gluons, protons, and neutrons…
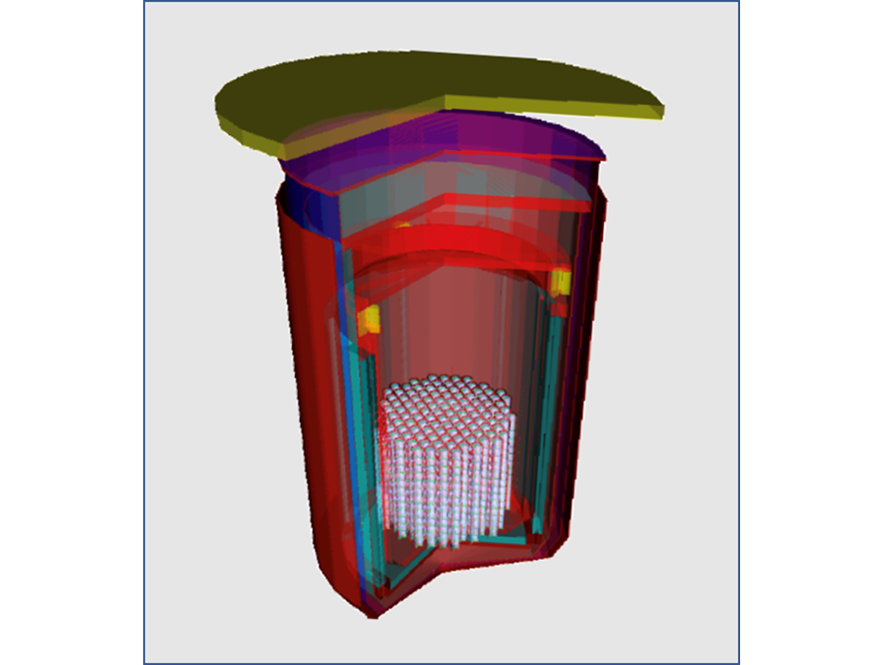
CUPID is an experiment to search for neutrinoless double beta decay (NLDBD). The DOE Nuclear Physics program granted Critical Decision Zero (CD-0, “mission need”) to the experiment in…

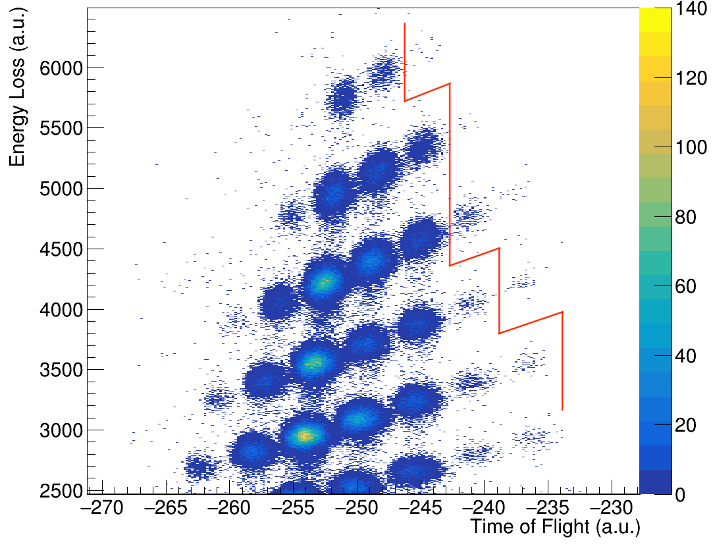
Many of the superheavy elements discovered in the last few decades were produced by bombarding heavy-element targets with high-current beams of neutron-rich isotopes like…
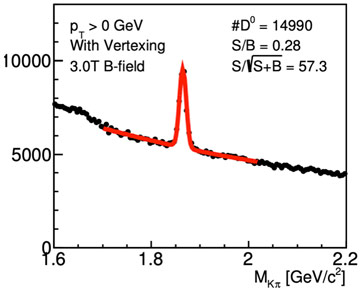
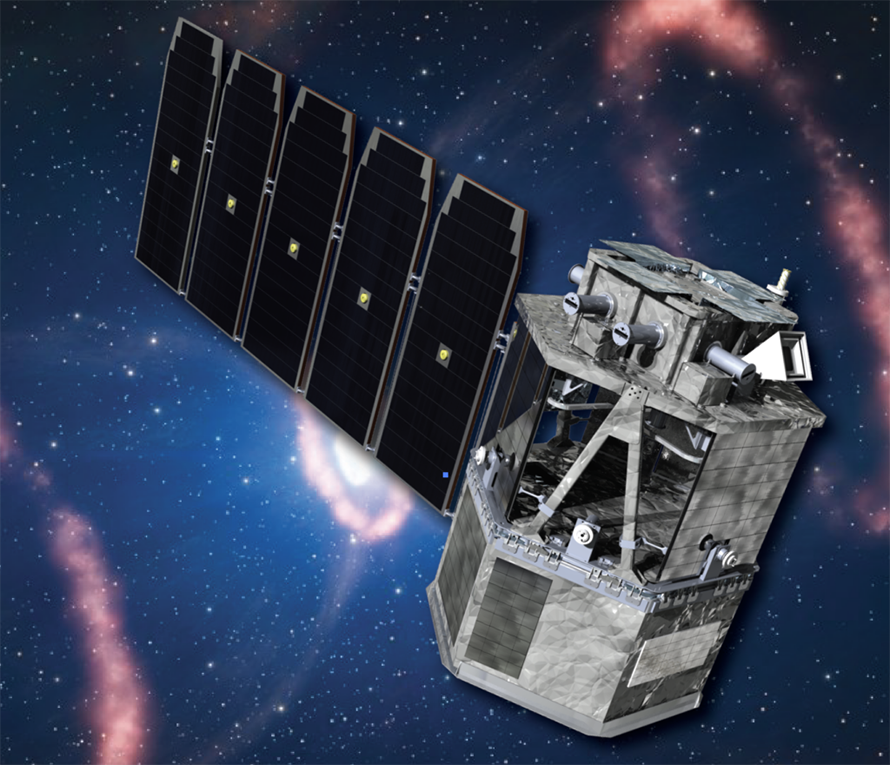
With CD-0 from the DOE and the formation of an Electron-Ion Collider (EIC) Project Office, experimental physicists are spending more time thinking about EIC detectors…
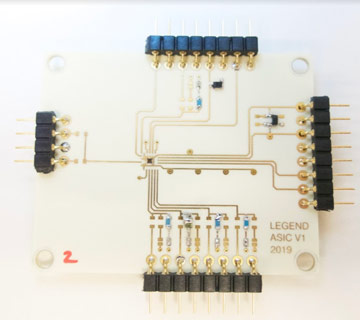
The Large Enriched Germanium Experiment for Neutrinoless Double Beta Decay (LEGEND) project is a next-generation experiment to search for the lepton-number-violating process neutrinoless double-beta decay (0νββ) in…
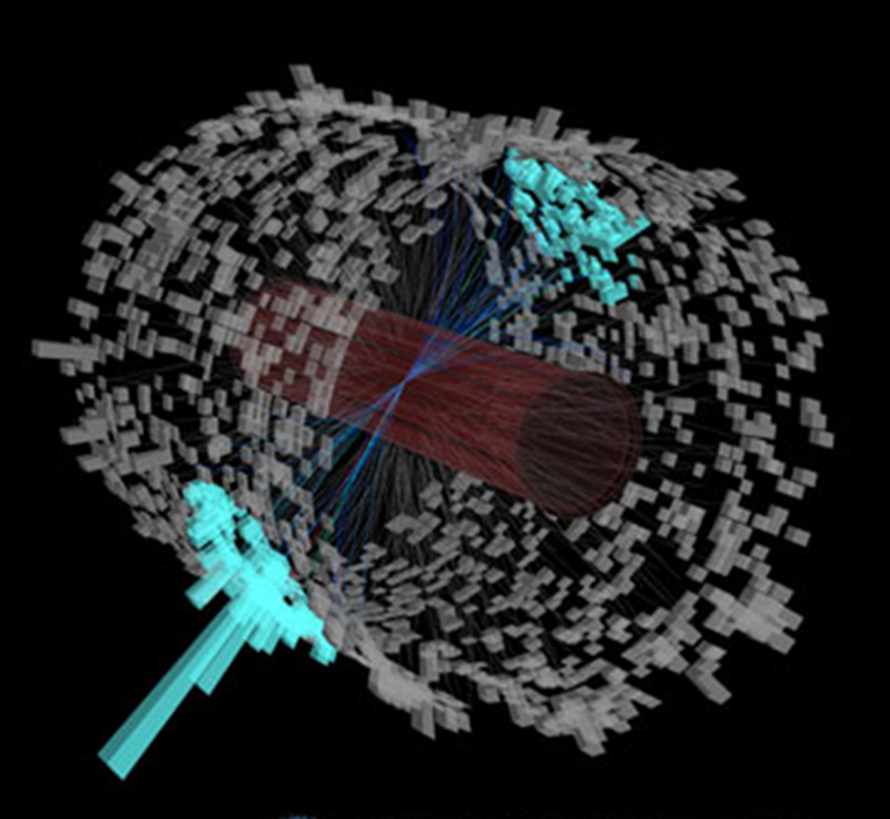
Collisions of heavy atomic nuclei at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at BNL and the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN generate tiny droplets of matter under conditions of…

With this issue, we are proud to introduce a new regular newsletter section “Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Moments,” highlighting recent Division DEI activities.

For the Nuclear Science Division (as for the lab as a whole), safety is our highest priority. So, most of us are working from home, on data analysis, simulations, writing, and other tasks…

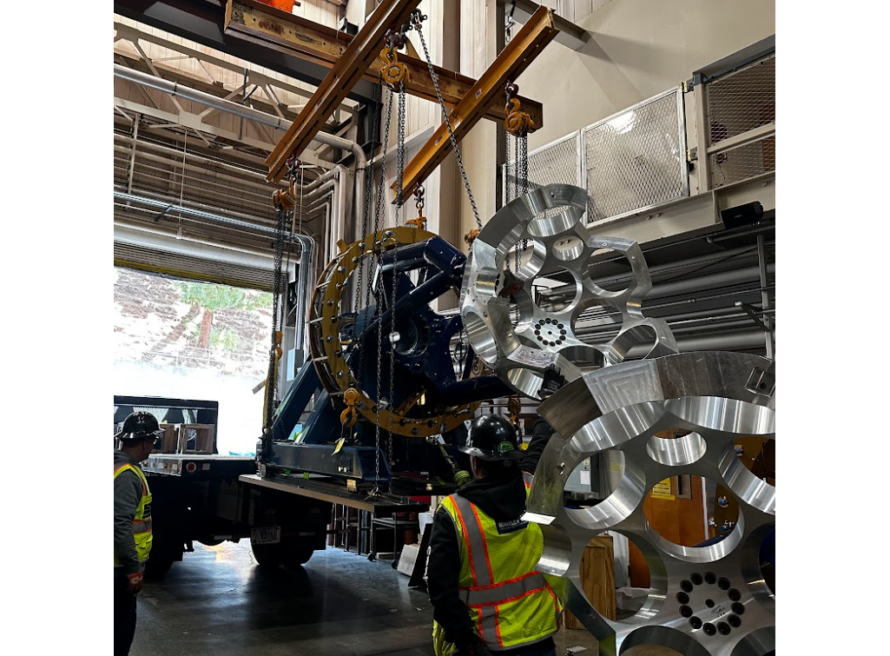
Gamma-Ray Energy Tracking Array (GRETA) is a 4π germanium tracking detector capable of reconstructing the energy and three-dimensional position of γ-ray interactions that will provide an unparalleled resolving power…