Spencer Klein, A.H. Mueller, Bo-Wen Xiao, Feng Yuan, Acoplanarity of Lepton Pair to Probe the Electromagnetic Property of Quark Matter, Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 132301 (2019)
We investigate the PT-broadening effects in dilepton production through photon-photon scattering in heavy ion collisions. The QED multiple interaction effects with the medium is found to be consistent with a recent observation of low transverse momentum lepton pair from ATLAS collaboration at the LHC. We further comment on the magnetic effects and point out a number of ways to disentangle these two mechanisms. In particular, the rapidity dependence of the PT-broadening effects provide a unique probe to the magnetic effects.
Jet quenching is considered one of the major discoveries in relativistic heavy ion experiments from RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory and the LHC at CERN. These phenomena have been well formulated in QCD, where the energy loss and PT -broadening effects are closely related. The parameter qhat has been extracted from various experimental data. Meanwhile, qhat*L describes the typical transverse momentum squared that a parton acquires in the medium of length L. In the last few years, there have been significant progress in understanding the PT -broadening effects in dijet, photon-jet, and hadron-jet productions in heavy ion collisions.
We extend our previous studies on the dijet azimuthal correlation (Phys.Lett. B763 (2016) 208-212) to the di-lepton correlation and focus on two main areas. One is the QED Sudakov effect, where we show that the theory prediction for the UPC events agree very well with data from ATLAS. Second, we investigate the medium effects, including the QED multiple interaction effects similar to the PT -broadening of the QCD jet and the magnetic effects. We also discuss how to disentangle these two mechanisms.
The comparison of the PT -broadening effects in QCD and QED is of crucial importance to understand the medium property in heavy ion collisions. The lepton’s PT -broadening effects is sensitive to the electromagnetic property of the quark-gluon plasma, whereas the jet PT -broadening effects depends on the strong interaction property. The experimental and theoretical investigations of both phenomena will deepen our understanding of the hot medium created in these collisions. The clear measurements of lepton PT -broadening effects from ATLAS and STAR should stimulate further study on dijet azimuthal correlations in heavy ion collisions.
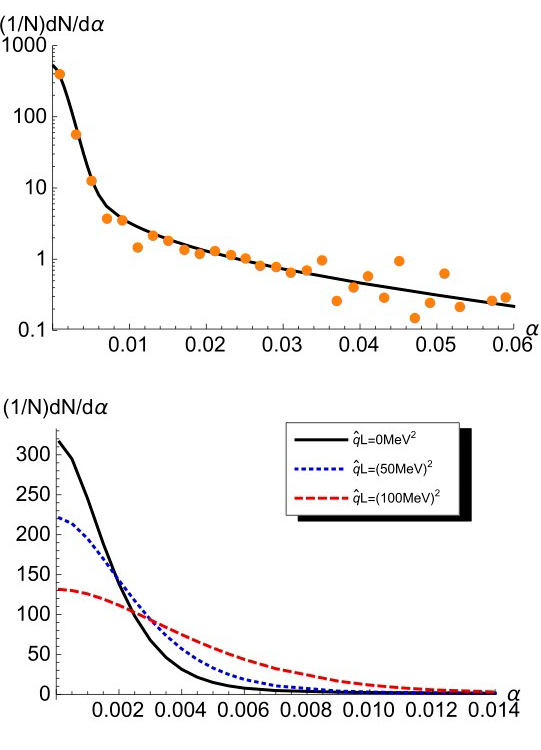 Upper Figure: Acoplanarity distribution for lepton pair production at mid-rapidity in UPC events at the LHC with a typical kinematics: lepton transverse momentum P⊥ > 4 GeV and pair invariant mass from 10 to 100 GeV. The detailed explanation of different curves is provided in the main text. The total contribution with resummation (solid curve) agrees well with the ATLAS measurement.
Upper Figure: Acoplanarity distribution for lepton pair production at mid-rapidity in UPC events at the LHC with a typical kinematics: lepton transverse momentum P⊥ > 4 GeV and pair invariant mass from 10 to 100 GeV. The detailed explanation of different curves is provided in the main text. The total contribution with resummation (solid curve) agrees well with the ATLAS measurement.
Lower Figure: Medium modifications to the acoplanarity distribution, with different values of the effective qL.